missing translation for 'onlineSavingsMsg'
Learn More
Learn More
Description
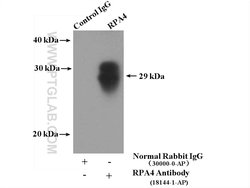
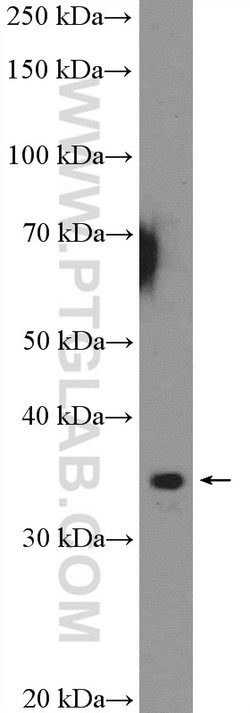
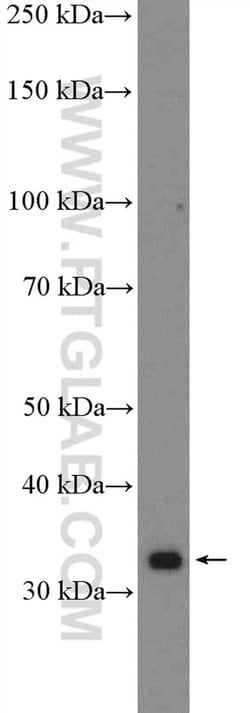
The single-stranded-DNA-binding proteins (SSBs) are essential for DNA function in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, mitochondria, phages and viruses. Replication protein A (RPA), a highly conserved eukaryotic protein, is a heterotrimeric SSB consisting of three subunits that play an important role in DNA replication, recombination and repair. RPA is one of the major damage- recognition structures involved in the early stage of nucleotide excision repair and may function in telomere maintece. The binding of human RPA (hRPA) to DNA involves molecular polarity, in which initial hRPA binding occurs on the 5′ side of a ssDNA substrate and then extends in the 3′ direction to create a stably bound hRPA. Widely expressed at low to intermediate levels,RPA 34 kDa subunit, which is also known as RPA4 (replication factor A protein 4), contains 261 amino acids, localizes to nucleus and is preferentially expressed in mucosa of colon and placenta.
Specifications
Specifications
| Antigen | RPA4 |
| Applications | Immunoprecipitation, Western Blot |
| Classification | Polyclonal |
| Concentration | 0.22 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Formulation | PBS with 50% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide; pH 7.3 |
| Gene | RPA4 |
| Gene Accession No. | Q13156 |
| Gene Alias | HSU24186, Replication factor A protein 4, replication protein A4, 34kDa, RF A protein 4, RP A p30, RPA4 |
| Gene Symbols | RPA4 |
| Show More |
Product Title
By clicking Submit, you acknowledge that you may be contacted by Fisher Scientific in regards to the feedback you have provided in this form. We will not share your information for any other purposes. All contact information provided shall also be maintained in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
Spot an opportunity for improvement?