missing translation for 'onlineSavingsMsg'
Learn More
Learn More
Description
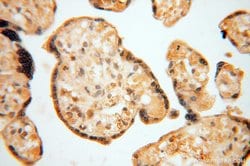
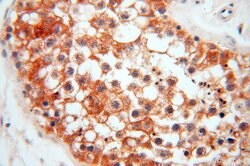
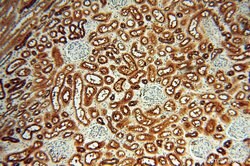
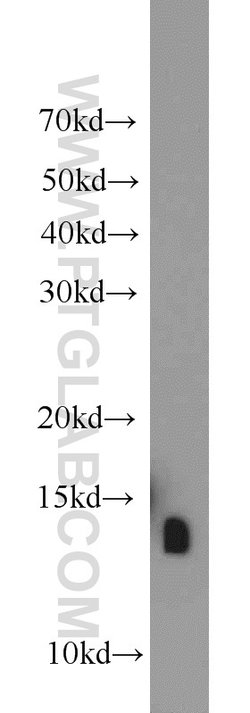
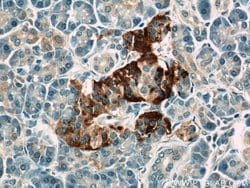
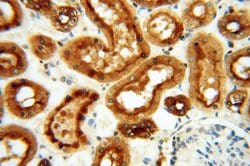
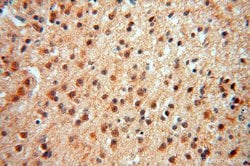
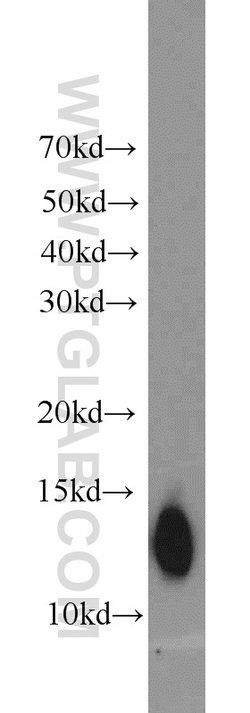
ATP6V1F encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPase dependent organelle acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A and three B subunits, two G subunits plus the C, D, E, F, and H subunits. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The V0 domain consists of five different subunits: a, c, c′, c", and d. Additional isoforms of many of the V1 and V0 subunit proteins are encoded by multiple genes or alternatively spliced transcript variants. This encoded protein is the V1 domain F subunit protein.
Specifications
Specifications
| Antigen | ATP6V1F |
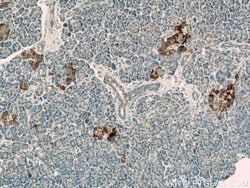
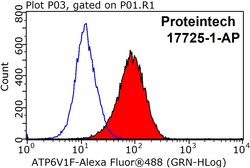
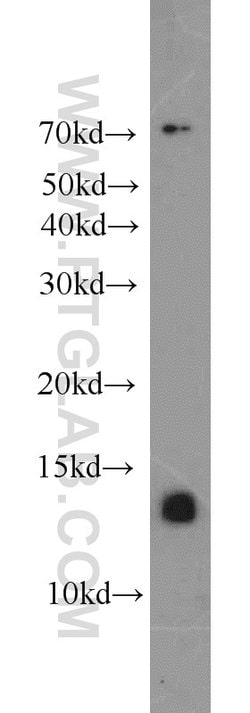
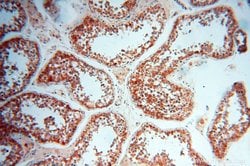
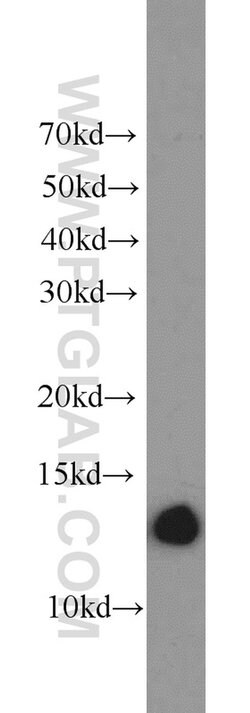
| Applications | Western Blot, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Flow Cytometry |
| Classification | Polyclonal |
| Concentration | 0.31 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Formulation | PBS with 50% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide; pH 7.3 |
| Gene | ATP6V1F |
| Gene Accession No. | Q16864, Q9D1K2 |
| Gene Alias | ATP6S14, ATP6V1F, V ATPase 14 kDa subunit, V ATPase subunit F, V type proton ATPase subunit F, Vacuolar proton pump subunit F, VATF, Vma7 |
| Gene Symbols | Atp6v1f |
| Show More |
Product Title
By clicking Submit, you acknowledge that you may be contacted by Fisher Scientific in regards to the feedback you have provided in this form. We will not share your information for any other purposes. All contact information provided shall also be maintained in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
Spot an opportunity for improvement?